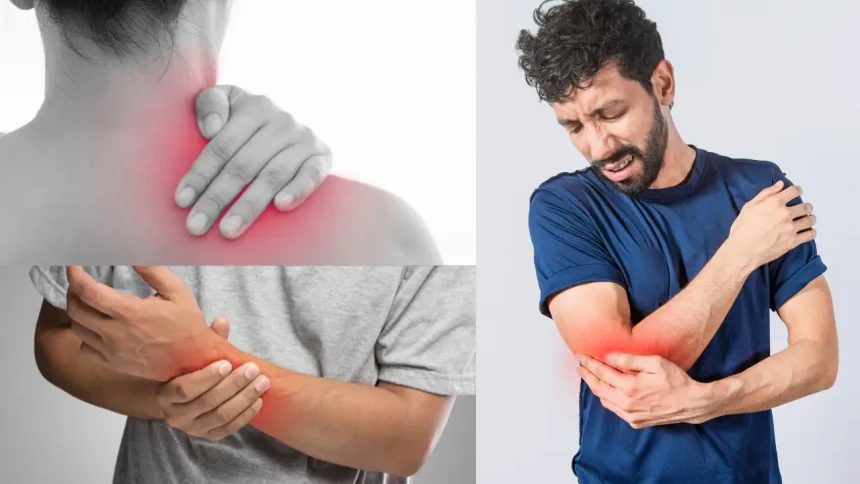
Shoulder, elbow, wrist pain are common musculoskeletal issues that can significantly affect daily activities and quality of life. Shoulder pain often arises from injuries to the rotator cuff, impingement, or arthritis, and can be triggered by repetitive overhead movements, trauma, or poor posture. It is typically felt as aching or sharp pain in the shoulder joint, with restricted motion. Elbow pain, often caused by conditions like tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) or golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis), results from overuse or repetitive motion, especially in activities that involve gripping or twisting. This pain is usually localized to the outer or inner side of the elbow and may be accompanied by weakness or difficulty with everyday tasks. Wrist pain can stem from injuries such as sprains, fractures, or repetitive strain injuries like carpal tunnel syndrome, where pressure on the median nerve causes pain, numbness, and tingling. Arthritis and tendonitis are also common causes of wrist discomfort. In all cases, treatment often involves rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Early diagnosis and proper management are key to preventing long-term damage and ensuring recovery.
Causes Of Shoulder Pain
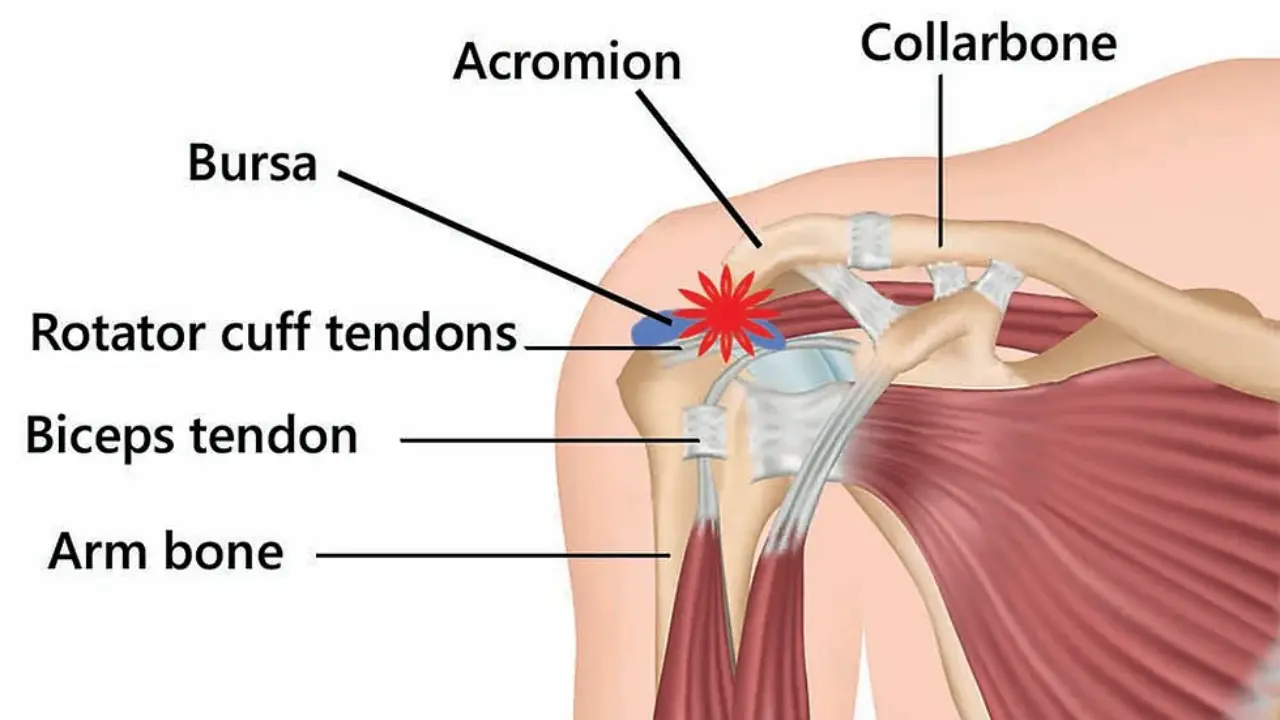
- Arthritis in the shoulder joint
- Bone spurs in the shoulder area
- Bursitis, which is inflammation of a fluid-filled sac (bursa) that normally protects the joint and helps it move smoothly
- Broken shoulder bone
- Dislocation of the shoulder
- Shoulder separation
- Frozen shoulder, which occurs when the muscles, tendons, and ligaments inside the shoulder become stiff, making movement difficult and painful
- Overuse or injury of nearby tendons, such as the bicep muscles of the arms
- Nerve injury that leads to abnormal shoulder movement
- Tears of the rotator cuff tendons
- Poor shoulder posture and mechanics
Causes Of Elbow Pain
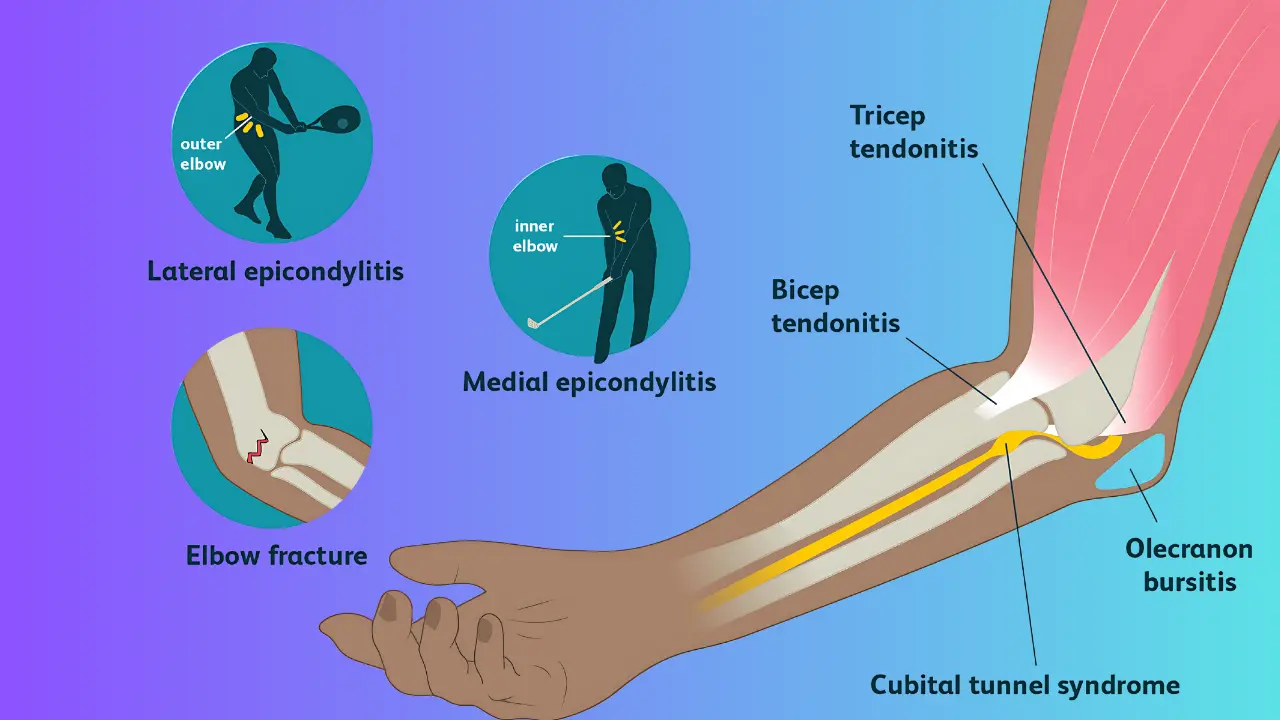
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis):
Inflammation of the outer elbow tendons due to repetitive gripping or arm movements.
Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis):
Pain on the inner side of the elbow caused by repetitive forearm and wrist motions.
Bursitis:
Inflammation of the bursa (fluid-filled sac) in the elbow, often due to prolonged pressure or trauma.
Arthritis:
Degenerative changes in the elbow joint, leading to pain and stiffness (commonly osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis).
Fractures:
Broken bones in the elbow, often from trauma or falls, leading to severe pain and immobility.
Nerve Compression (Cubital Tunnel Syndrome):
Pressure on the ulnar nerve, causing pain, numbness, and tingling in the elbow and hand.
Causes Of Wrist Pain
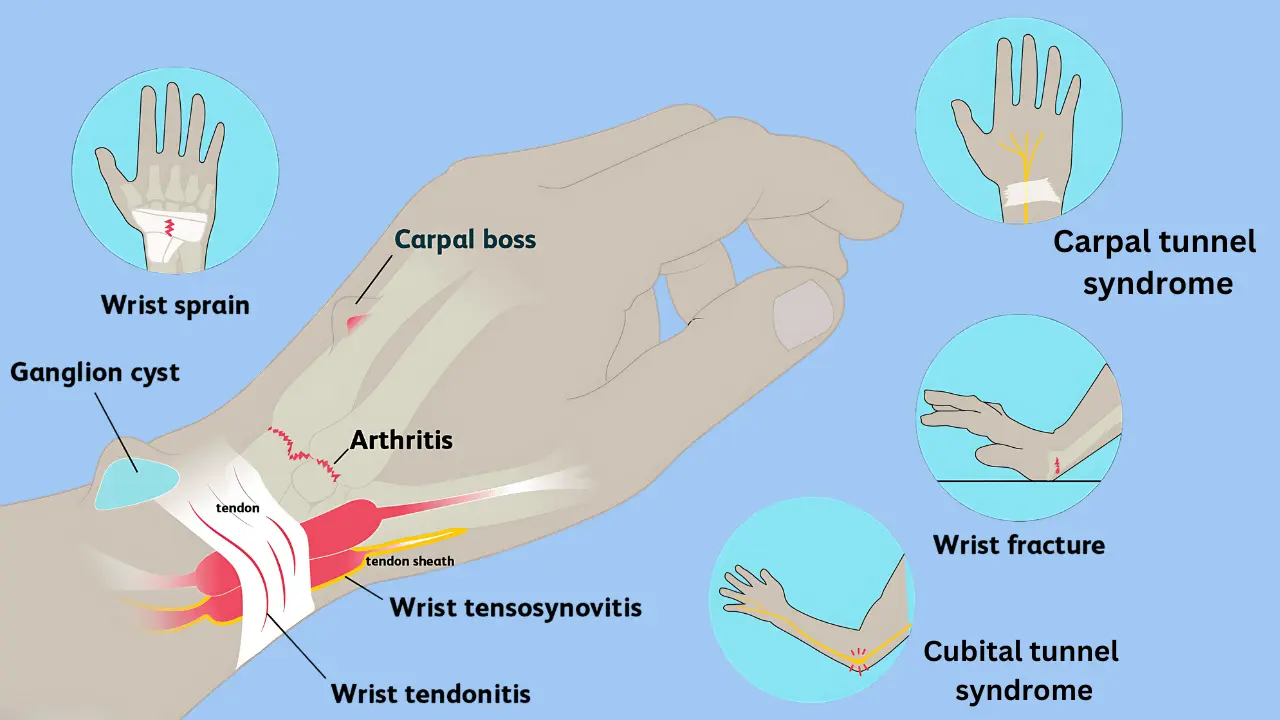
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
Compression of the median nerve in the wrist, leading to pain, tingling, and numbness, often from repetitive use.
Tendonitis:
Inflammation of the wrist tendons, commonly from repetitive motions or overuse, such as De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis.
Wrist Sprains:
Ligament injuries caused by falls or sudden twisting motions.
Arthritis:
Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis affecting the wrist joint, causing pain and stiffness.
Fractures:
Broken bones in the wrist, often caused by falls or trauma, particularly involving the radius or scaphoid.
Ganglion Cysts:
Treatment For Shoulder, Elbow and Wrist Pain
Treatment for Shoulder, Elbow, and Wrist Pain
Treatment for shoulder, elbow, and wrist pain varies based on the underlying cause, but generally includes a combination of rest, physical therapy, medications, and in some cases, surgical interventions. Below are common treatment options for each area:
Shoulder Pain Treatment
Rest and Ice:
Resting the shoulder and applying ice for 15–20 minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and pain, especially after activity or injury.
Physical Therapy:
Stretching and strengthening exercises to improve range of motion, stability, and function. Therapy can also help in post-surgery rehabilitation.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Corticosteroid Injections:
In cases of severe inflammation or conditions like rotator cuff tendinitis or bursitis, a steroid injection can provide significant pain relief.
Surgery:
Surgery may be required for severe rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement, or frozen shoulder. Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive option for many shoulder conditions.
Heat Therapy:
Applying heat may help relieve chronic shoulder stiffness and pain.
Elbow Pain Treatment
Rest and Ice:
Resting the elbow and applying ice to reduce swelling and inflammation in conditions like tennis elbow or golfer’s elbow.
Physical Therapy:
Exercises to stretch and strengthen the forearm muscles and tendons can help reduce pain and improve function. Eccentric exercises are often prescribed for tendonitis.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen can be used to manage pain and inflammation.
Bracing or Splinting:
A wrist splint or elbow brace can provide support and reduce strain on the affected tendons, particularly in conditions like tennis elbow.
Corticosteroid Injections:
For more severe pain, corticosteroid injections may help reduce inflammation in the elbow joint or tendons.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
This involves injecting platelet-rich plasma into the elbow to promote healing of damaged tendons, commonly used in tendonitis cases.
Surgery:
If conservative treatments fail, surgery may be needed to repair torn tendons, remove damaged tissue, or address nerve compression (e.g., cubital tunnel syndrome).
Wrist Pain Treatment
Rest and Ice:
Resting the wrist and applying ice for 15–20 minutes to reduce swelling and inflammation, especially after activity or injury.
Wrist Splints or Braces:
Wrist braces or splints help immobilize the wrist to reduce strain and allow the ligaments, tendons, and nerves to heal (especially for conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or tendonitis).
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and swelling, especially for conditions like arthritis or tendonitis.
Physical Therapy:
Targeted exercises and stretches can help improve wrist strength, flexibility, and functionality, especially after injuries or surgeries.
Corticosteroid Injections:
Corticosteroid injections may be used for conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or arthritis to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
Ergonomic Adjustments:
For conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, ergonomic changes to workstation setup (keyboard/mouse placement) and proper wrist positioning can help reduce strain.
Surgery:
Surgery may be necessary for severe conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome (to release pressure on the median nerve), wrist fractures, or arthritis that do not respond to conservative treatments. For ganglion cysts, surgical removal may be considered if the cyst causes persistent pain or dysfunction.