Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health, supporting immune function, and regulating various metabolic processes in the body. It is naturally obtained from sunlight, certain foods (like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods), and supplements.
Vitamin D supplements are commonly used to address or prevent deficiency, especially for individuals who have limited sun exposure, live in regions with low sunlight, or have conditions that affect the absorption of vitamin D (such as osteoporosis, certain gastrointestinal disorders, or chronic kidney disease).
Benefits Of Vitamin D Boots
It seems like you’re asking about the benefits of Vitamin D boots. However, it’s unclear whether you’re referring to a specific type of footwear designed to help with vitamin D absorption (which doesn’t really exist) or you might be asking about the benefits of Vitamin D supplementation or boosting your vitamin D levels in general. I’ll assume you meant the latter, but if you were referring to something specific, feel free to clarify!
Benefits of Boosting Vitamin D Levels
Vitamin D is a vital nutrient that plays a significant role in a range of bodily functions. Boosting your vitamin D levels, especially if you’re deficient, can have several health benefits. Here’s a breakdown of the main advantages:
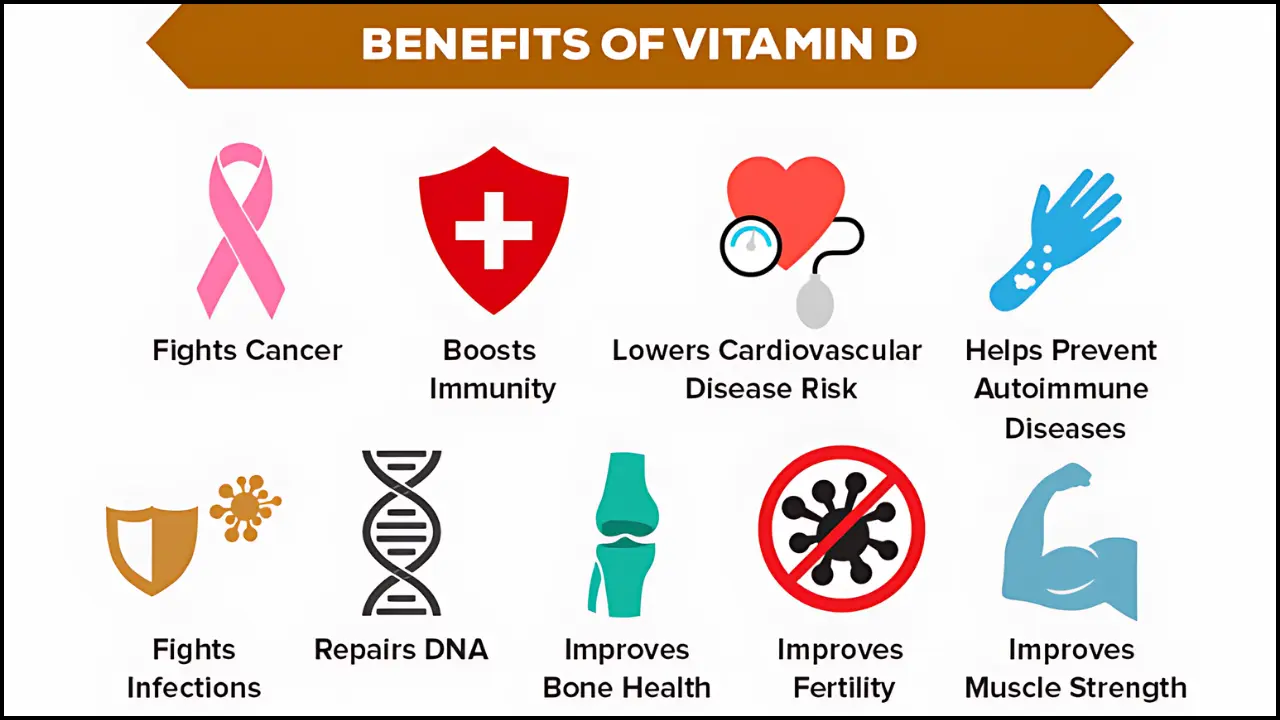
Bone Health
Calcium Absorption:
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, which is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth.
Prevention of Osteoporosis:
Adequate levels of vitamin D can help prevent conditions like osteoporosis, where bones become brittle and fragile.
Rickets Prevention in Children:
For children, vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets, a condition where bones become soft and weak.
Fracture Prevention:
Studies suggest that adequate vitamin D levels help reduce the risk of falls and fractures, particularly in older adults.
Immune System Support
Strengthens Immunity:
Vitamin D plays a role in regulating the immune system, supporting your body’s ability to defend against infections.
Autoimmune Diseases:
There is some evidence suggesting that vitamin D deficiency might be linked to autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis. Adequate levels may help lower the risk.
Mood and Mental Health
Depression:
Vitamin D has been linked to mood regulation. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with depression, particularly seasonal affective disorder (SAD), which occurs in the winter months when sunlight exposure is limited.
Cognitive Function:
Some studies suggest that vitamin D might play a role in maintaining brain health, and there is evidence linking deficiency to cognitive decline and an increased risk of diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Muscle Strength and Function
Vitamin D contributes to the function of muscles by aiding in muscle contraction and strength. Low levels ofvitamin D are associated with muscle weakness, which can lead to a higher risk of falls, especially in older adults.
Cardiovascular Health
Heart Health:
Some studies suggest that vitamin D may help lower the risk of heart disease, although the research is still ongoing. Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to increased risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including high blood pressure, heart attack, and stroke.
Blood Pressure Regulation:
Vitamin D may play a role in regulating blood pressure by influencing how blood vessels function.
Weight Loss and Metabolism
Some research indicates that adequate vitamin D levels may support weight loss and healthy metabolism. Low vitamin D levels have been associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome, though more research is needed in this area.
Cancer Prevention
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that vitamin D may help lower the risk of certain cancers, including breast, prostate, and colon cancer, by regulating cell growth and preventing uncontrolled cell proliferation.
Type 2 Diabetes Management
Vitamin D plays a role in insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity. Adequate levels of vitamin D may help improve the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, potentially reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Support for Pregnancy
Adequate vitamin D levels during pregnancy are important for both maternal health and fetal development. Vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy has been linked to complications such as pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes, and low birth weight.
Symptoms Of Vitamin D Deficiency
The majority of people Trusted Source with a vitamin D deficiency do not have symptoms. However, a chronic deficiency may cause osteomalacia, which may lead to Trusted Source:
- bone pain
- joint pain
- muscle weakness or spasms
- problems with bone development or the teeth
- Over time, weakened bones may contribute to osteoporosis and increase the risk of falls and fractures, especially in older adults.
Sources Of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for bone health, immunity, and overall well-being. The primary source is sunlight, as the skin produces vitamin D when exposed to UV rays. Dietary sources include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna, which are rich in vitamin D. Fortified foods such as milk, cereals, and orange juice also provide significant amounts. Additionally, egg yolks and mushrooms exposed to sunlight are good natural sources. For those with limited sun exposure, supplements can help maintain adequate vitamin D levels.
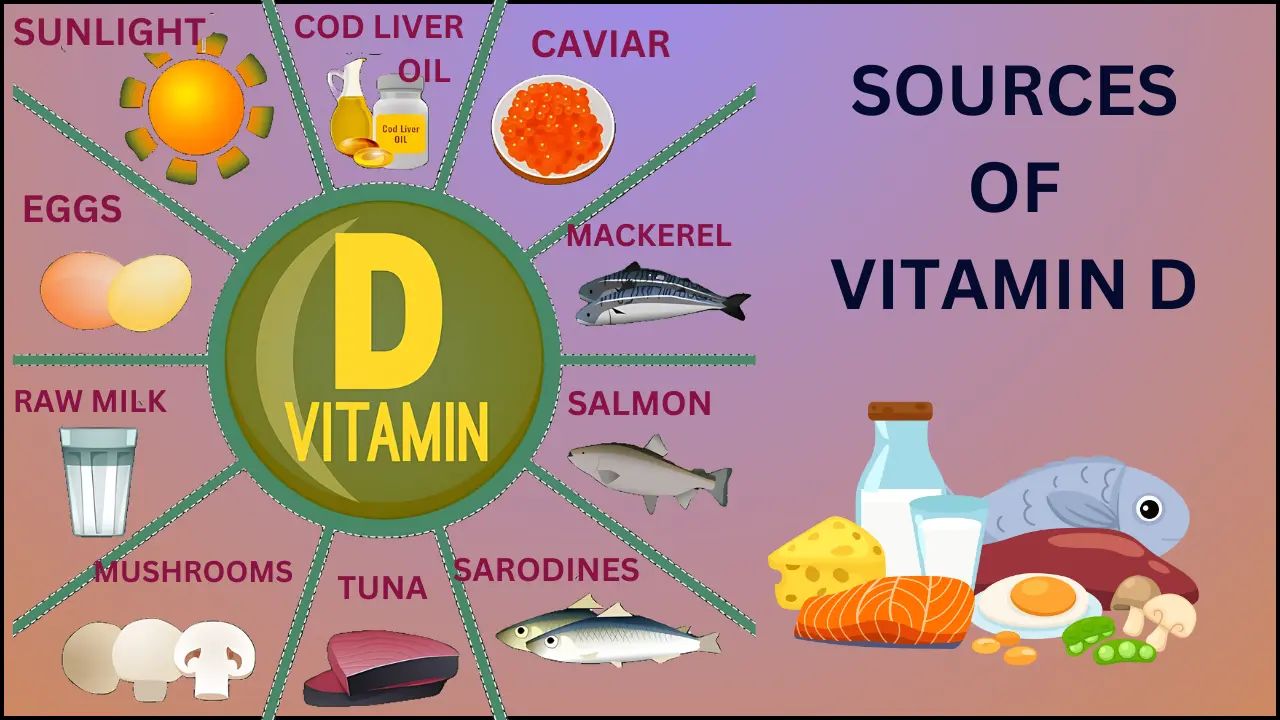
The following foods provide some vitamin D, too:
- fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and tuna
- egg yolks
- cheese
- beef liver
- mushrooms
- fortified milk
- fortified cereals and juices
Vitamin D Boots Pharmacy FAQ’S
Q1. Why is vitamin D important?
Ans. Vitamin D contributes to the maintenance of normal bones, muscles, and teeth, and supports the normal function of the immune system. It also aids in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, which are vital for bone health.
Q2. Should I take a vitamin D supplement?
Ans. During autumn and winter, it’s advised that adults and children over five years of age take a daily supplement of 10 µg (400 IU) of vitamin D to maintain adequate levels. This helps keep your immune system, bones, teeth, and muscles healthy.
Q3. What forms of vitamin D supplements are available at Boots?
Ans. Boots offers a variety of vitamin D supplements, including tablets, capsules, and liquid forms, catering to different preferences and needs. These supplements are available in various strengths to suit individual requirements.
Q4. Are there any side effects of taking vitamin D supplements?
Ans. When taken as directed, vitamin D supplements are generally safe. However, excessive intake can lead to side effects such as hypercalcemia (high levels of calcium in the blood), which may cause nausea, vomiting, and kidney problems. Always adhere to the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns.


