Knee and Ankle Pain
Physical therapists have an extensive knowledge of knee and ankle issues that can trigger pain. The fact that you’re feeling knee pain and ankle pain in the same leg can help them narrow down that list. A few of the issues that more commonly cause this combo of pain are:
Osteoarthritis
This condition is caused by progressive wear and tear on your joints. Often, repetitive movements you do are a major factor in developing osteoarthritis. Why? They wear out the cartilage in your joints. This can lead to inflammation and joint bones rubbing against each other, which can both trigger pain. Athletes, truck drivers and warehouse workers are a few examples of people who are more likely to develop knee and ankle osteoarthritis.
A joint injury
You might think that the pain of a joint injury would only affect the injured joint. Yet that’s not always the case. Nerves allow pain signals to be sent from the injured area into other areas of the body. Pain that starts in one place and moves into another is known as radiating pain.
Let’s say you sprained your ankle. It’s possible that the pain of that injury could radiate into your calf and reach your knee. Such an injury could also lead to movement changes and other issues that could also trigger knee pain.
A pinched or irritated nerve
As previously mentioned, nerves allow pain signals to travel through the body. Pinching or irritation of your nerves can be the source of such pain signals. For instance, a person with a pinched sciatic nerve could experience widespread radiating pain. Typically, sciatica pain starts in the lower back, but the sciatic nerve runs all the way down your legs. As a result, sciatica pain can radiate all the way down to your feet.
Causes Of Knee And Ankle Pain
The important causes of knee and ankle pain are as follows:
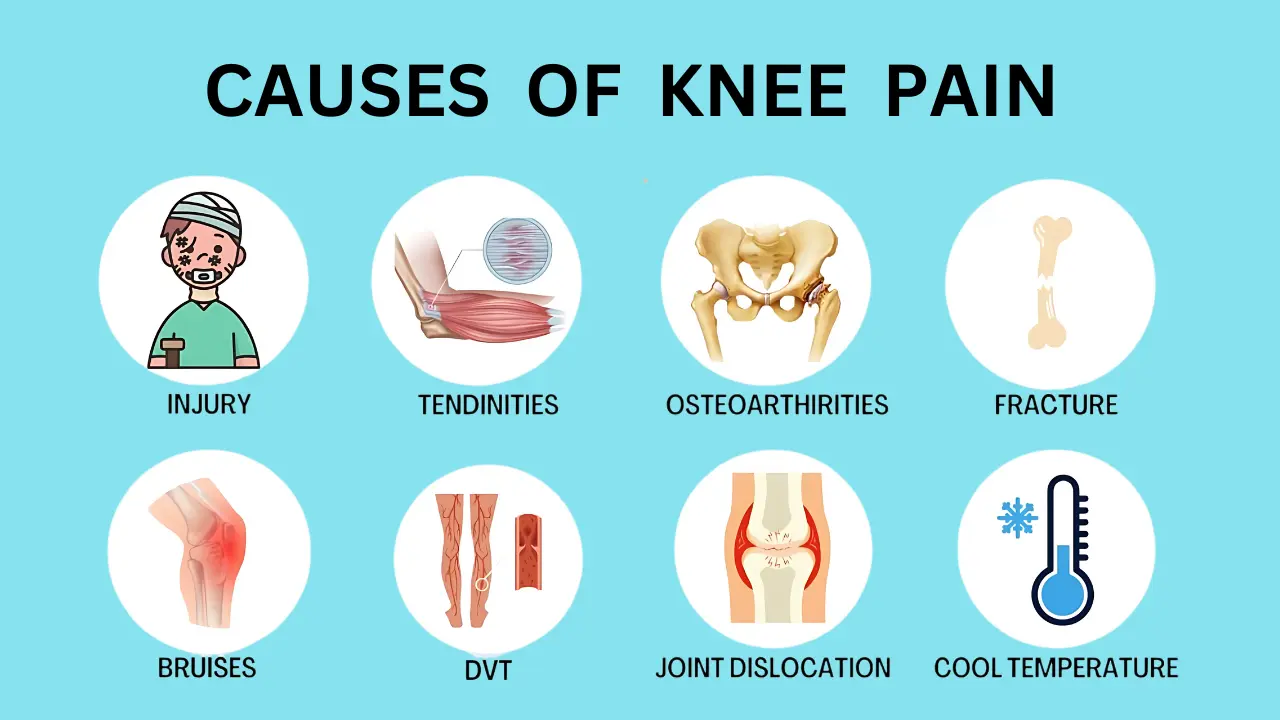
Knee Pain Causes:
Injuries:
Sprains, strains, and meniscus tears are common.
Arthritis:
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis lead to joint inflammation and pain.
Tendinitis:
Inflammation of tendons, such as patellar tendinitis.
Bursitis:
Inflammation of the bursae around the knee.
Patellar Issues:
Conditions affecting the kneecap and its alignment.
Ankle Pain Causes:
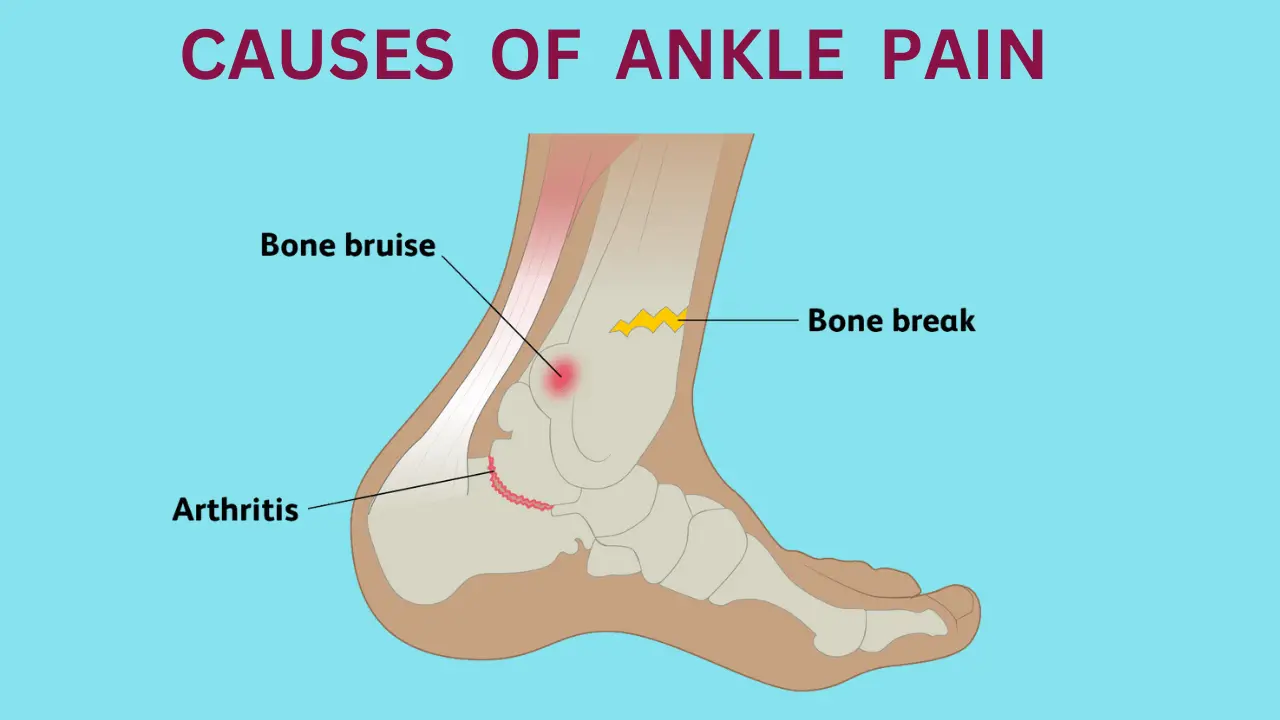
Injuries:
Ankle sprains and fractures are frequent causes.
Tendinitis:
Overuse can lead to inflammation of the ankle tendons.
Arthritis:
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the ankle joint.
Achilles Tendon Issues:
Tendinitis or ruptures can cause significant pain.
Gout:
Uric acid buildup can result in sudden, severe ankle pain.
Knee And Ankle Pain Treated
Rest and Activity Modification:
Avoid activities that exacerbate pain.
Modify movements to reduce strain on the affected joint.
Ice Therapy:
Apply ice packs for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce swelling and pain.
Compression:
Use elastic bandages or braces to provide support and decrease swelling.
Elevation:
Keep the affected joint elevated above heart level to help reduce swelling.
Pain Relief Medications:
Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy:
A physical therapist can design a program to strengthen the muscles around the joint and improve flexibility.
Injections:
Corticosteroid injections may provide relief for inflammation and pain.
Hyaluronic acid injections can help lubricate the joint, especially for osteoarthritis.
Orthotics:
Custom shoe inserts or braces can provide support and improve alignment.
Lifestyle Changes:
Weight management can reduce stress on the joints.
Low-impact exercises (like swimming or cycling) can help maintain fitness without putting excessive strain on the joints.
Surgery:
In severe cases, surgical options like arthroscopy, ligament repair, or joint replacement may be necessary.
Preventing Knee And Ankle Pain
Preventing knee and ankle pain involves a combination of lifestyle choices, proper techniques, and regular maintenance of joint health. Here’s a detailed explanation of effective prevention strategies:
Stay Active:
Regular Exercise:
Engage in low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, or walking to maintain joint flexibility and strength. Regular movement helps keep joints lubricated and functional.
Strengthen Muscles:
Targeted Exercises:
Focus on strengthening the muscles around the knees and ankles. Exercises such as squats, lunges, and calf raises can enhance stability and support, reducing the risk of injury.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Weight Management:
Excess body weight increases stress on the knees and ankles. Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly decrease the risk of joint pain and injury.
Wear Supportive Footwear:
Proper Shoes:
Invest in shoes that offer good arch support, cushioning, and fit. This helps absorb shock and maintain proper alignment, which is crucial for joint health.
Warm Up and Stretch:
Pre-Exercise Routine:
Always warm up before physical activity to prepare your muscles and joints. Include stretching to enhance flexibility and reduce the risk of strains.
Modify Activities:
Listen to Your Body:
Pay attention to discomfort or pain during activities. Modifying high-impact exercises or avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can prevent injuries.
Use Proper Techniques:
Correct Form:
When exercising or participating in sports, use proper techniques to reduce the risk of injury. Consider working with a coach or trainer to ensure correct form.
Rest and Recover:
Rest Days:
Allow adequate time for recovery between workouts to prevent overuse injuries. Incorporating rest days helps muscles and joints recover and rebuild.
Incorporate Balance Training:
Balance Exercises:
Activities like yoga or tai chi can improve balance and stability, which helps prevent falls and injuries, particularly in older adults.
Stay Hydrated:
Hydration:
Drinking enough water supports joint lubrication and overall health. Proper hydration can help maintain joint function and reduce stiffness.
Symptoms of knee and ankle pain
Knee and ankle pain can result from a variety of causes, including injuries, degenerative conditions, and other underlying health issues. Here’s an overview of some common factors:
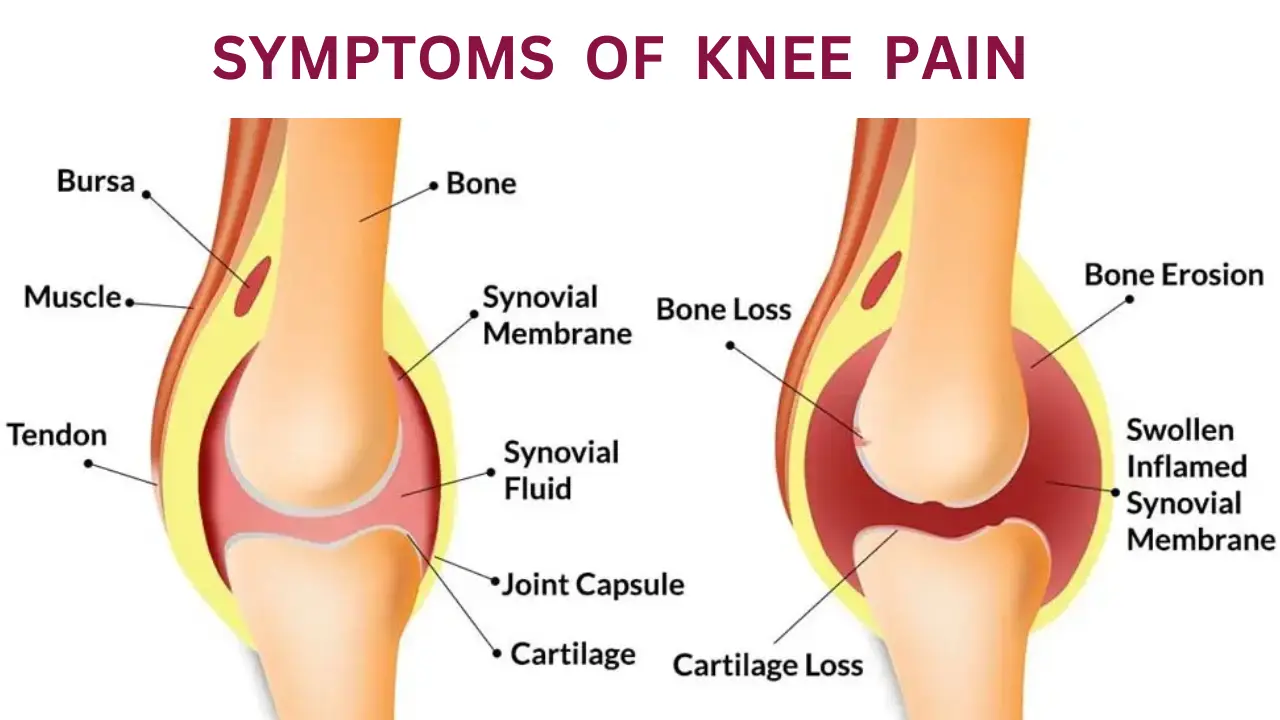
Knee Pain
Injuries:
ACL Tears:
Often occur in sports, causing sudden pain and swelling.
Meniscus Tears:
Can happen during twisting motions:
symptoms include pain and stiffness.
Patellar Tendonitis:
Inflammation of the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone, often seen in athletes.
Degenerative Conditions:
Osteoarthritis:
Wear and tear of cartilage leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
An autoimmune disorder causing inflammation in joints, including the knees.
Other Conditions:
Bursitis:
Inflammation of the bursa (fluid-filled sacs) around the knee.
Iliotibial Band Syndrome:
Tightness in the iliotibial band can cause pain on the outside of the knee.
Ankle Pain
Injuries:
Sprains:
Twisting the ankle can stretch or tear ligaments, leading to pain and swelling.
Fractures:
Breaks in the bones of the ankle can cause severe pain and inability to bear weight.
Degenerative Conditions:
Osteoarthritis:
Similar to the knee, this can occur in the ankle, leading to joint pain and stiffness.
Achilles Tendonitis:
Inflammation of the tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel, often resulting from overuse.
Other Conditions:
Tendinitis:
Inflammation of tendons around the ankle due to repetitive movements.
Gout:
A type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid, leading to sudden, severe pain, often in the big toe but can affect the ankle.